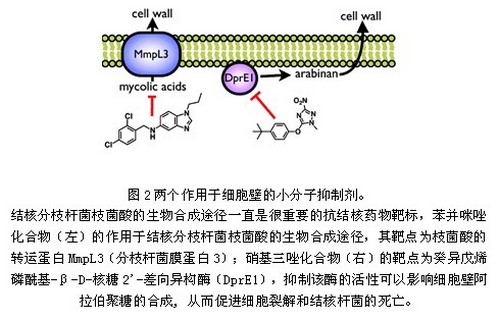
The tuberculosis known as the "white plague" is a chronic infectious disease transmitted through the respiratory tract. It mainly occurs in the lungs and is an important international infectious disease. In recent years, due to population growth and increased mobility, the emergence of MDR-TB and XDR-TB, HIV / AIDS infection and transmission, etc. Even worse, tuberculosis has once again become one of the most serious epidemics threatening the safety and health of the entire world. With the support of the Gates Fund-Global Anti-Tuberculosis Alliance, Genzyme Pharmaceuticals and the Chinese Academy of Sciences Knowledge Innovation Project, Zhang Lixin ’s research group conducted a systematic study on anti-tuberculous mycobacterial active ingredients in marine microorganisms in China and found that Many anti-tuberculosis compounds with new mechanisms of action. Due to the slow growth of wild M. tuberculosis strain H37Rv, which affects the efficiency of high-throughput screening, the research team constructed a high-throughput screening model for logarithmic growth phase BCG vaccine (BCG, attenuated strain of M. bovis) , Can directly read the fluorescence to determine the growth of bacteria, greatly reducing the time required for testing. Relying on the strain library and natural product crude extract library that have been established in the laboratory, through high-throughput screening, the researchers obtained a series of crude extracts with good activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, amplified fermentation of these active strains, Activity tracking separation, obtained a series of components with good activity. These research results have been applied for patents, and related articles have been published in Organic Letters, Journal of Natural Products and other international natural product magazines. Among them, through cooperation with Professor Robert Capon of the University of Queensland, Australia, four new active compounds were found from a strain of marine fungus, one of which is a unique dimer compound with the strongest anti-BCG activity. The minimum inhibitory concentration is 6.25µg / mL, and the minimum bacteriostatic concentration of other microorganism strains tested is greater than 100μg / mL. The selectivity of its biological activity and the potential for the creation of a completely new mechanism of action brought about by the unique structural framework have attracted attention. The research results were recently published in Organic Letters (OL) (Figure 1). The research team cooperated with the Broad Institute of the United States to establish a M. tuberculosis whole-cell screening model, and successfully screened and identified two small molecule inhibitors from the natural product library of the research group, and revealed their targets by chemical biology Related to cell wall formation, the research results were published in the journal ACS Chemical Biology (Figure 2). The paper was published online less than one month ago and has entered the journal Most viewed article. The biosynthetic pathway of mycobacterium tuberculosis mycolic acid has always been an important target for anti-tuberculosis drugs. Transporter MmpL3 (Mycobacterium membrane protein 3); the target of the nitrotriazole compound (right) is decyl isopentenylphosphoryl-β-D-ribose 2-epimerase (DprE1), which inhibits The activity of the enzyme can affect the synthesis of arabinan in the cell wall, thereby promoting cell lysis and the death of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The researchers of the research group also published anti-tuberculosis compounds with new structures in other journals. The research group was also invited by Natural Product Reports magazine to summarize and review the research on active ingredients against TB. Frying Basket Strainer,Deep Fryer Strainer Basket,Fryer Mesh Basket,Stainless Steel Fry Basket HOMEARTS INDUSTRIAL CO.,LTD , http://www.homeartschina.com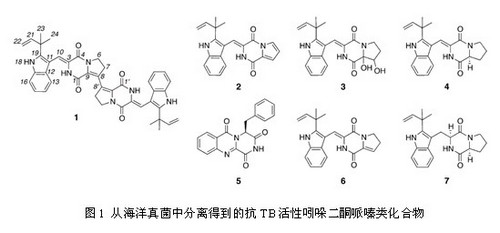
New progress has been made in the screening of anti-tuberculosis drugs