In the above four processes, the latter two are mainly used in our engineering examples, but even so, the effluent CODcr of the ink waste water is still high, generally 400-800 mg/L. Since the ink waste water accounts for about 5% of the total water, it is pretreated. After the ink waste water is discharged into the total water, it will still cause the CODcr of the total water to exceed the standard. Therefore, the effluent after the ink pretreatment needs to be further processed to reduce the CODcr as much as possible. Generally, the final effluent CODcr after the ink waste water treatment is required. 200mg/L can ensure that the total effluent CODcr after PCB wastewater treatment is lower than 100mg/L. In reaching the project, the ink waste water is pressure-filtered through the plate and frame, the filtrate is adjusted to neutrality, and then biological treatment is performed. The entire process flow of the ink waste water treatment is as follows. The above process should be applied in the project, and the treatment effect is better. The acidification and slag removal mainly removes the film materials in the ink wastewater, and can be removed by about 50% (the higher the original water concentration, the higher the removal rate), the coagulation reaction and the plate frame Filter press mainly removes suspended matter, copper and part of CODcr, the removal rate of suspended matter and copper can reach over 90%, CODcr removal accounts for about 30% of total CODcr, and anaerobic and aerobic mainly removes organic matter from ink wastewater, and can be removed. CODcr accounts for about 15% of total organic matter. The total process removal of ink wastewater CODcr is about 95-98%, and the effluent CODcr can be as low as 150mg/L or less. Note that for anaerobic and aerobic biological treatment, some organic wastewater with better biochemical properties (nutrition may also be added) should be properly added to improve the biodegradability of ink wastewater. 4 Conclusion
Process C is applied to the printed circuit board wastewater treatment project of Yaoyong Electronics Co., Ltd. The total design scale of the project is 800 tons/day, of which ink waste water is about 30 tons/day. The influent CODcr of the ink wastewater of this plant is about 8000-12000 mg/L, which can reach 400-600 mg/L after air flotation, and the CODcr removal rate can reach 95%. Ink wastewater is removed by acidification to remove most of the scum. After processing, PH is added to adjust the pH to about 8.5. The PAC and PAM coagulants are added to the flotation equipment for coagulation reaction. The ink wastewater is reacted in the flotation equipment. Under the action of the dissolved air in the district, a solid-liquid separation is formed, the slime floats on the top, and the clear liquid flows out of the bottom drain pipe. Using this process to treat PCB ink waste water, the effect is better, the management is convenient, the air-floating water is very clear, transparent and colorless. However, its power consumption is high and the amount of sludge is large. This process is suitable for PCB ink wastewater with high concentration.
Process D is applied to the circuit board wastewater treatment project of Dajin Electronics Co., Ltd. The total design scale of the project is 13200 tons/day, the scale of the first phase is 6600 tons/day, and the ink waste water is about 300 tons/day. The influent CODcr of the ink wastewater of this plant is 1000-4000 mg/L. After the plate and frame filtration, the CODcr of the filtrate is 600-800 mg/L, and the CODcr removal rate is about 70-80%. The process of ink wastewater after acidification, there are a large number of colloidal ink precipitation, scraped by an automatic scraper, the water is added to the lye to neutralize, adjust the pH to 9 or so, while adding PAC and PAM, stirred by the air The mixed reaction is turned into a mixed liquid, which is then driven by a screw press pump into the plate and frame filter press. The ink and suspended matter in the waste water are retained in the plate and frame filter press, and the filtrate is discharged. This process has a good effect on the treatment of ink waste water, the water is clear, the processing volume is large, and it is easy to operate and manage.
The above four processes have been applied to different projects. The acidification unit mainly removes most of the film materials. After the acidification and slag removal, the suspended solids of the wastewater are still high, and the removal rate of CODcr is only 40-50%. Further condensation and separation are needed. In addition to CODcr, SS, and copper, based on engineering experience, the following compares the advantages and disadvantages of the four processes. 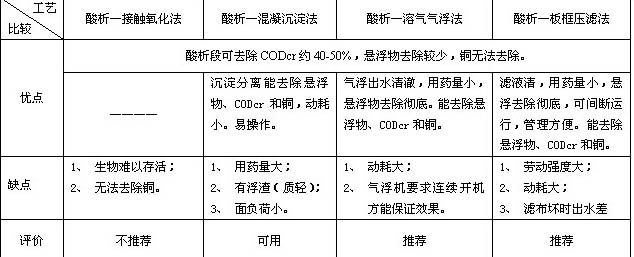

PCB ink waste water is a kind of difficult-to-treat high-concentration organic waste water, which is very important for the complete factor discharge of the circuit board wastewater treatment project. In particular, removal of CODcr from PCB ink waste water is difficult to reach below 100 mg/L in general. Therefore, we must conduct in-depth research and practice on the characteristics of PCB ink wastewater and the ingredients it contains to select and determine a more mature and feasible treatment process. Experimental studies and engineering practices lead to the following conclusions that can be used for engineering design.
1. The amount of ink waste water accounts for about 5% of the total printed circuit board waste water, and the CODcr contribution to all waste water reaches 80%. The ink waste water treatment must be separated from the workshop to separate the water and drain, completely separated, and must not be disorderly arranged and avoided as much as possible. Other low-concentration waste water or copper-containing waste water is mixed in. Low-concentration waste water will cause an increase in the amount of ink waste water. The biological treatment of copper-bearing waste water is difficult.
2, ink wastewater is generally alkaline, pH 9-12, using acid precipitation method to remove the film material, the pH should be adjusted to 2-3, will consume a lot of acid, the project can use the production line discharged waste acid solution The pH value of the ink waste water will achieve the purpose of waste treatment and waste, which will save considerable drug costs.
3. Ink wastewater contains pollutants such as COD, SS, and copper. Ink wastewater treatment process should take into account the removal of these pollutants. Acid precipitation can remove COD. Coagulation can remove copper to avoid the toxic effects of copper on organisms. After acidification and coagulation, the COD is still very high, and the biochemical treatment is used. Since the BOD/COD value is too low (<0.2), organic matters and nutrient salts must be added properly. In the project, domestic wastewater from the plant can be taken into consideration. Improve the biodegradability of ink waste water.
Author: Yan Yonghong ... Source: Guangdong Dayu Environmental Engineering Co., Ltd.
PCB ink wastewater treatment process research and engineering practice (2)
Process B is applied to the board wastewater treatment project of Hongban Electronics Co., Ltd. The total design scale is 1200 tons/day, of which the ink waste water is about 50 tons/day. According to the long-term operation monitoring, the ink wastewater CODcr is about 3000-4000 mg. / L, after the precipitation can generally reach 1000 mg/L, CODcr removal rate of up to 75%. In the treatment process, there are often more scums in the ink waste water sedimentation tank during operation, which is mainly due to the fact that the photosensitive film and other organic substances in the PCB ink waste water are light in specific gravity and are not easily precipitated. Therefore, in order to achieve the desired treatment effect, the surface loading of the sedimentation tank should be selected to be smaller, not exceeding 0.6m3/m2.h, and correspondingly increase the investment cost of civil works (or equipment).